Acne Treatment
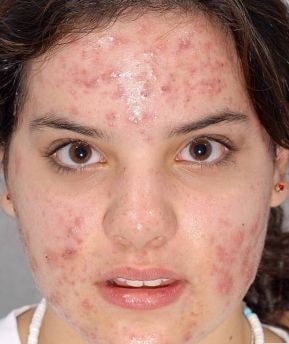

What is the pathophysiology?
The key factor is genetics. If both parents had acne, 3 of 4 children will have acne.
Androgen hormones have been implicated as the initial trigger, clinical lesions begin to appear around puberty in persons with acne.
Androgen hormones promote sebum production and release.
Pacnes is an anaerobic organism present in acne lesions. The presence of P acnes promotes inflammation through a variety of mechanisms.
What is the role of diet?
Comprehensive review of the literature in 2004 concluded that there was no conclusive evidence on the effects of diet on acne.
These studies failed to support a link between the consumption of chocolate or sugar and acne. Thus, no evidence exists on the role of diet in acne.
Numerous dairy sources and foods with high glycemic indices, appears to have solidly-documented potentiating effects on serum insulin and IGF-1 levels, thereby promoting androgens that could potentiate a change in sebum production and therefore inflammation and acne.
More research is needed to determine whether a low-glycemic diet could effectively mediate acne or possibly even prevent it.
At what age dose acne appear?
Adolescent acne usually begins with the onset of puberty, when the gonads begin to produce and release more androgen hormone.
Acne is not limited to adolescence. Twelve percent of women and 5% of men at age 25 years have acne. By age 45 years, 5% of both men and women still have acne.
What are the causes of acne?
Presence of hormonal imbalances (polycystic ovary syndrome, oral contraceptives, exogenous androgens). Systemic medications (anabolic or corticosteroids, OCPs, psychiatric medications). Corticosteroid-containing skin-bleaching agents that are used by some individuals with darker skin (especially in some African populations) to improve hyperpigmentation or lighten complexion may induce steroid acne, which may further worsen PIH. Occlusive topical agents Mechanical irritation Self-manipulation of lesions (picking). The role of diet, sun exposure, and smoking are controversial.
What are the presentations?
Comedonal-non inflammatory: open (black heads) or closed (white heads) 1 -2 mm papules Inflammatory: papules and pustules and cysts Nodular: require systemic retinoids Scarring acne: require systemic retinoids How can I prevent acne? If you have oily skin: benzoyl peroxide (2.5-10%) or salicylic acid (0.5-2%) acne wash. It may not be necessary to use it every day, especially if you experience excessive dryness. If you have dry skin: you may not need to wash your face at all unless you have combination skin (dry/oily) or wear make-up or creams during the day. Use a non-comedogenic (non-pore clogging) cold cream, gentle moisturizing face wash or non- fragrance containing soap to remove make-up. Hair products that contain oils – including shampoo, conditioner, hair spray, hair gel, pomade – may cause acne on the forehead, sides of the face, or neck (with long hair). It is recommended that you shampoo & condition your hair in the shower, followed by cleansing of the face in the sink with cool or lukewarm water. Do not use a washcloth, loofah, or other abrasive scrub. Choose a non-comedogenic (non-pore clogging) sunscreen with zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide if you have acne-prone skin or if you experience skin irritation with other chemical-containing sunscreens.
What are the available medical treatments?
Eliminate participating factors.
Topical treatments: wash the skin with cold or luke warm water. Cleanse with prescribed cleanser. Wait 20 min before applying the medication. Apply a pea-sized amount of med. To the entire face and then gently connecting the dots with your fingertips.
Retin A:
Note that acne often flares during the first month of using topical retinoids. They also make the skin more sensitive to sun. Therefore, non-comedogenic sunscreen should be used during the day.
Benzoyl peroxide: wash, gel, lotion, or pads (2.5-10%)
Antibiotics: erythromycin 2% or clindamycin
Azelaic acid (15 or 20% cream) b.i.d. and topical or systemic erythromycin base are safe alternatives in patients desiring pregnancy, for PIH, and has comedolytic effect
Additional comedolytic effect can be achieved by addition of products containing
Salicylic acid 2% topical gel, lotion, or wash or a 10-30% in-office peel
Glycolic acid 2.5-20% topical gel, lotion, wash, or in-office peel
Topical sodium sulfacetamide (10% lotion, gel or wash such as Plexion, Rosac, Rosanil, Rosula, or Sulfacet-R) is a good alternative, especially in acne in adult female patients with peri-oral accentuation.
Oral antibiotics:
The tetracycline group of antibiotics is commonly prescribed for acne. The more lipophilic antibiotics, such as doxycycline and minocycline, are generally more effective*
than tetracycline
Doxycycline hyclate 100 mg once or twice daily
Oral contraceptive pills in females
Corticosteroids
Short courses (7-10 days) of systemic steroids (prednisone 20-40 mg/day) will abort flares* at critical times (weddings, proms, interviews, etc.).
Inflammatory lesions may be treated with intralesional corticosteroids (e.g. triamcinolone acetonide 2.5–5.0 mg/cc), which usually result in improvement within 2–5 days by reducing inflammation.*
Isotretinoin (Roaccutane®)
Isotretinoin is used to treat severe, disfiguring nodular acne. It should be used only after other acne medicines have been tried and have failed to help the acne. The treatment course should be at least 5 months* and should reach the desired full dose of 120 mg/kg. Most patients tolerate between 0.75 mg/kg. About 85% of patients see clear skin after one course of treatment with isotretinoin.
Isotretinoin is a teratogen, and pregnancy must be avoided.
Contraception counseling is mandatory, and 2 negative pregnancy test results are required prior to the initiation of therapy in women of childbearing potential. The baseline laboratory examination should also include cholesterol and triglyceride assessment, hepatic transaminase levels, and a CBC count. Pregnancy tests and laboratory examinations should be repeated monthly during treatment.
What are the consequences?
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Acne scars.